Beware: Fake CAPTCHA Campaign Spreads Lumma Stealer in Multi-Industry Attacks
In an increasingly connected world, cyber threats continue to evolve, posing significant risks across industries and geographies. One recent alarming development is the fake CAPTCHA campaign leveraging Lumma Stealer malware. This malicious strategy deceives users into executing harmful commands, making it essential for organizations and individuals to understand and safeguard against such attacks. With its sophisticated techniques and global impact, this campaign highlights the urgent need for robust cybersecurity practices.
Understanding the Fake CAPTCHA Campaign
The fake CAPTCHA campaign is a sophisticated phishing tactic that exploits user interactions to bypass browser-based security measures and deliver malware payloads. It represents a new breed of attacks where traditional security defenses often fall short.
How the Attack Works
- Initial Compromise:
- Users encounter compromised websites redirecting them to fake CAPTCHA pages.
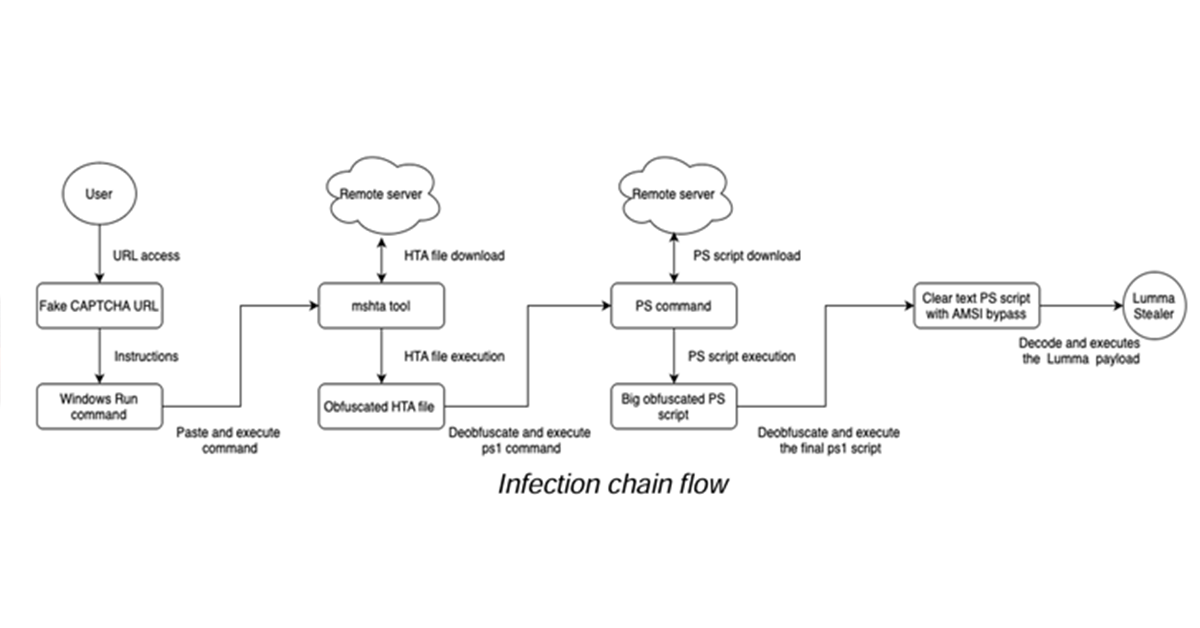
- These CAPTCHA pages instruct users to copy and paste a command into their Windows Run prompt, initiating the attack.
- Malware Execution:
- The command uses the
mshta.exebinary to download a malicious HTA file from a remote server. - This file executes multiple PowerShell scripts designed to decode and deploy the Lumma Stealer payload.
- The command uses the
- Avoiding Detection:
- The malware disables the Windows Antimalware Scan Interface (AMSI), a critical component of Windows’ security framework.
- This bypass strategy ensures the payload executes without triggering browser-based defenses or other automated detection systems.
Industries and Regions Affected
The campaign has impacted multiple sectors, including:
- Healthcare: Targeting sensitive patient data and financial information.
- Banking: Exploiting access to accounts and transactional systems.
- Marketing: Compromising client data and communication channels.
- Telecommunications: Experiencing the highest number of organizational targets due to their critical infrastructure roles.
Global regions such as the United States, Argentina, Colombia, and the Philippines have reported significant targeting. This demonstrates the widespread appeal and adaptability of the campaign, posing a severe threat across international borders.
The Lumma Stealer: Malware-as-a-Service (MaaS)
Lumma Stealer is a Malware-as-a-Service offering, gaining popularity among threat actors due to its adaptability and effectiveness. This service model lowers the entry barrier for less-skilled attackers, enabling widespread distribution.
Key Characteristics of Lumma Stealer
- Delivery Mechanisms:
- Fake CAPTCHA pages redirecting to HTA files.
- Approximately 1,000 counterfeit domains mimicking popular services like Reddit, WeTransfer, and AnyDesk.
- Password-protected archives containing droppers designed to execute the malware.
- Payload Behavior:
- Uses advanced PowerShell scripts for decoding and deploying malware.
- Employs AutoIT droppers (e.g., SelfAU3 Dropper) to execute the stealer while evading detection.
Why It’s Hard to Detect
- Constant evolution of delivery methods and payloads ensures a high degree of adaptability.
- Advanced evasion techniques, such as AMSI bypasses, prevent detection by conventional antivirus tools.
- High reliance on user interaction, such as executing commands manually, makes automated detection challenging.
Broader Implications and Recent Trends
Phishing-as-a-Service (PhaaS): A Growing Threat
The fake CAPTCHA campaign is part of a broader trend of PhaaS toolkits like Tycoon 2FA. These toolkits:
- Use legitimate or compromised email accounts for phishing campaigns.
- Detect and disrupt security tools during inspections, enhancing the effectiveness of phishing efforts.
- Leverage services like Gravatar to mimic trusted brands and harvest credentials.
PhaaS offerings are growing rapidly, with attackers constantly improving their techniques to bypass detection and exploit unsuspecting users.
Increased Sophistication in Social Engineering
Attackers now:
- Create convincing fake profiles on platforms like Gravatar to mimic trusted brands.
- Tailor their phishing pages to specific companies such as AT&T, Comcast, and Proton Mail.
- Use keystroke detection and other advanced techniques to identify and evade automated security tools.
Protecting Against Fake CAPTCHA Campaigns
Organizations and individuals must adopt proactive measures to mitigate risks:
Best Practices for Individuals
- Be Skeptical: Avoid copying and pasting commands from unverified sources or suspicious websites.
- Use Security Software: Install reputable antivirus tools and keep them updated.
- Educate Yourself: Learn to recognize phishing attempts and suspicious websites to reduce the risk of falling victim.
Best Practices for Organizations
- Invest in Employee Training: Conduct regular cybersecurity awareness programs to educate employees about emerging threats.
- Implement Advanced Threat Detection: Use tools that can detect PowerShell-based attacks and identify abnormal system behavior.
- Regularly Audit Infrastructure: Perform routine security audits to identify and remediate vulnerabilities in your network.
- Develop Incident Response Plans: Ensure your organization has a robust plan in place for addressing and mitigating potential breaches.
Conclusion
The fake CAPTCHA campaign is a stark reminder of the evolving nature of cyber threats. By understanding the tactics employed in these attacks and implementing robust preventive measures, both individuals and organizations can significantly reduce their risk of falling victim. In an age where cybersecurity threats are constant, staying vigilant, informed, and proactive is essential to safeguarding against such sophisticated threats. Collaboration between individuals, organizations, and cybersecurity professionals is key to combating this growing menace effectively.
Discover how to safeguard your systems against sophisticated phishing and malware attacks today.