Threat actors have been exploiting a recently disclosed zero-day vulnerability in Palo Alto Networks PAN-OS software since March 26, 2024, nearly three weeks before its public disclosure yesterday.
Palo Alto Networks’ Unit 42 division is monitoring this activity, dubbed Operation MidnightEclipse, attributing it to a single threat actor whose origin remains unidentified.
The security flaw, identified as CVE-2024-3400 (CVSS score: 10.0), is a command injection vulnerability allowing unauthenticated attackers to execute arbitrary code with root privileges on the firewall.
This vulnerability affects PAN-OS 10.2, PAN-OS 11.0, and PAN-OS 11.1 configurations with GlobalProtect gateway and device telemetry enabled.
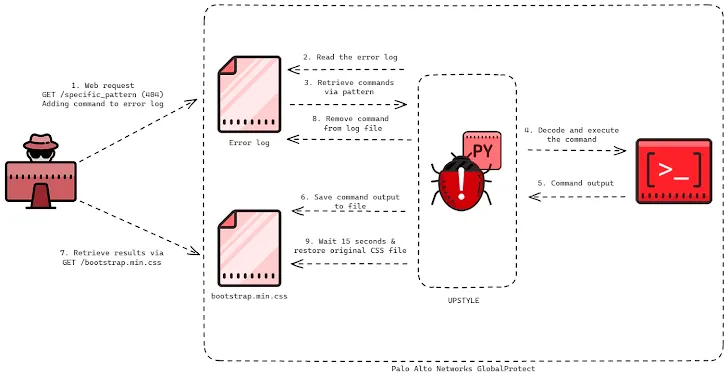
Operation MidnightEclipse involves exploiting this flaw to create a cron job that fetches commands from an external server (“172.233.228[.]93/policy” or “172.233.228[.]93/patch”) every minute, executing them via the bash shell.
Attackers manually manage an access control list (ACL) for the command-and-control (C2) server to restrict access solely to the communicating device.
While the exact nature of the commands remains undisclosed, it’s suspected that the URL serves as a delivery mechanism for a Python-based backdoor named UPSTYLE, hosted on a different server (“144.172.79[.]92” and “nhdata.s3-us-west-2.amazonaws[.]com”), according to Volexity, which discovered exploitation on April 10, 2024.
The Python file is designed to deploy and execute another Python script (“system.pth”), decoding and executing the embedded backdoor component, logging results in “sslvpn_ngx_error.log,” and writing operation outcomes to “bootstrap.min.css.”
Notably, both files are legitimate components of the firewall:
/var/log/pan/sslvpn_ngx_error.log
/var/appweb/sslvpndocs/global-protect/portal/css/bootstrap.min.css
The attack involves crafting network requests with a specific pattern to a non-existent web page, triggering the backdoor to parse the log file and execute commands.
The aim is to avoid leaving traces, necessitating exfiltration of results within 15 seconds before file overwriting.
Volexity observed the threat actor exploiting the firewall to create a reverse shell, download additional tools, pivot into internal networks, and exfiltrate data, although the full extent of the campaign remains unclear.
Organizations are advised to monitor Palo Alto Networks GlobalProtect firewall devices for signs of internal lateral movement.
The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) added the flaw to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog, mandating federal agencies to apply patches by April 19. Palo Alto Networks is expected to release fixes by April 14.
“Edge device targeting remains a favored tactic for capable threat actors,” Volexity noted, suggesting that UTA0218, the actor behind the exploitation, is likely state-backed due to the sophistication displayed in developing and exploiting such vulnerabilities and the nature of targeted victims.