A newly released proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit, dubbed LDAPNightmare exploit, has spotlighted critical security flaws in Windows Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP). These vulnerabilities, identified as CVE-2024-49113 and CVE-2024-49112, pose significant risks to organizations relying on Windows Server infrastructure. From denial-of-service (DoS) attacks to the potential for remote code execution (RCE), this exploit could disrupt business operations on a large scale if left unaddressed.
In this article, we delve deep into the technical intricacies of LDAPNightmare exploit, its implications for Windows servers, and the necessary steps to safeguard your infrastructure.
Understanding the LDAPNightmare Exploit
Key Vulnerabilities at a Glance
- CVE-2024-49113:
- Type: Out-of-bounds read vulnerability.
- Impact: Triggers a crash in the Local Security Authority Subsystem Service (LSASS), causing the system to reboot.
- Severity: Rated 7.5 on the CVSS scale.
- CVE-2024-49112:
- Type: Integer overflow vulnerability.
- Impact: Enables remote code execution within the LDAP service context.
- Severity: Rated 9.8 on the CVSS scale.
Both vulnerabilities were discovered by independent security researcher Yuki Chen (@guhe120) and addressed by Microsoft in their December 2024 Patch Tuesday updates. The PoC exploit, developed by SafeBreach Labs, was designed to highlight the criticality of these vulnerabilities.
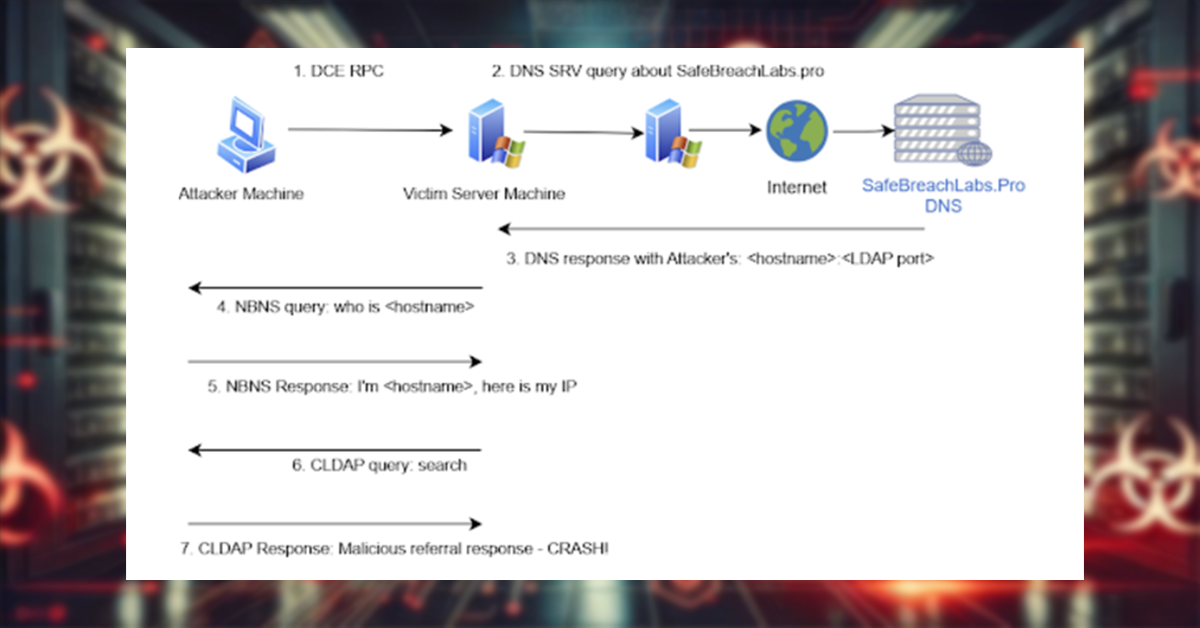
How LDAPNightmare Exploits the Vulnerabilities
LDAPNightmare exploit leverages vulnerabilities in the Windows LDAP implementation to cause severe disruptions:
- Denial-of-Service (DoS):
- A specially crafted CLDAP referral response is sent with a non-zero
lm_referralvalue. - This response crashes the LSASS process, leading to an automatic reboot of the target server.
- A specially crafted CLDAP referral response is sent with a non-zero
- Remote Code Execution (RCE):
- By modifying the CLDAP packet, attackers exploit CVE-2024-49112, enabling arbitrary code execution.
- This could allow an attacker to compromise the LDAP service and gain access to sensitive resources.
Prerequisites for Exploitation
The PoC demonstrates that LDAPNightmare exploit is relatively simple to execute:
- The victim’s Windows Server must be unpatched.
- The domain controller’s DNS server must have Internet connectivity.
This low barrier to exploitation increases the urgency for organizations to apply the necessary security patches.
Why LDAPNightmare Exploit Is a Significant Threat
Targeting Domain Controllers
Windows Domain Controllers are vital components in enterprise networks, managing authentication, authorization, and directory services. The exploitation of these servers can lead to:
- Authentication Disruptions: LSASS crashes result in server reboots, potentially halting authentication services.
- Data Breaches: Successful RCE can allow attackers to extract sensitive data or plant malware.
- Operational Downtime: Repeated server crashes can cripple business-critical operations.
Broader Implications
LDAP vulnerabilities are particularly dangerous due to the protocol’s central role in managing network resources. A compromised LDAP service can open doors to a variety of attacks, including lateral movement within the network, privilege escalation, and even ransomware deployment.
Mitigation Strategies
Apply Patches Immediately
Microsoft’s December 2024 updates address both vulnerabilities. Organizations must prioritize these updates to eliminate the risk of exploitation.
Temporary Workarounds
For scenarios where immediate patching isn’t possible, consider the following measures:
- Monitor Suspicious Traffic:
- Watch for anomalous CLDAP referral responses, particularly those with unexpected
lm_referralvalues. - Track unusual DsrGetDcNameEx2 calls and DNS SRV queries that may indicate exploit attempts.
- Watch for anomalous CLDAP referral responses, particularly those with unexpected
- Restrict RPC Access:
- Limit DCE/RPC access from untrusted networks.
- Implement firewall rules to block unauthorized LDAP traffic.
- Harden LDAP Configurations:
- Enforce secure LDAP (LDAPS) connections.
- Disable unauthenticated RPC calls wherever feasible.
Long-Term Defense Measures
- Network Segmentation:
- Isolate domain controllers and sensitive resources from the broader network.
- Use VLANs or subnetting to limit exposure.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention:
- Deploy systems to detect unusual LDAP activity.
- Regularly update threat intelligence feeds to stay ahead of emerging exploits.
- Regular Security Audits:
- Conduct routine vulnerability assessments to identify and address weak points.
- Use penetration testing to simulate attacks and test defenses.
Lessons from LDAPNightmare Exploit
Collaboration Is Key
The cybersecurity community’s collaboration, from Yuki Chen’s discovery to SafeBreach Labs’ PoC, highlights the importance of shared knowledge in addressing vulnerabilities. Organizations must stay informed through trusted channels like Microsoft’s advisories and industry research reports.
The Importance of Proactive Security
LDAPNightmare exploit underscores the risks of delayed patch management. Cybercriminals are increasingly targeting foundational protocols like LDAP, exploiting even minor misconfigurations.
Conclusion
The LDAPNightmare PoC exploit serves as a wake-up call for organizations relying on Windows Server infrastructure. With its ability to cause LSASS crashes and enable remote code execution, this exploit poses significant risks to enterprise operations.
While Microsoft’s patches provide a direct solution, the broader lesson is clear: cybersecurity is an ongoing process. By applying timely updates, monitoring network activity, and strengthening access controls, organizations can defend against emerging threats like LDAPNightmare exploit.
Summary: Key Takeaways
- Vulnerabilities: CVE-2024-49113 causes DoS, while CVE-2024-49112 enables RCE.
- Exploit Details: LDAPNightmare exploits LDAP flaws to disrupt Windows servers.
- Mitigation: Apply December 2024 patches, monitor suspicious traffic, and restrict untrusted RPC access.
Stay informed about the latest cybersecurity threats by subscribing to our newsletter. Share this article to raise awareness and help secure enterprise networks globally.