North Korean Hackers Unleash OtterCookie Malware in Contagious Interview Campaign
North Korean threat actors continue to expand their cyber arsenal with the deployment of a new JavaScript malware named OtterCookie Malware. This sophisticated malware is central to an ongoing hacking campaign dubbed Contagious Interview, which uses social engineering tactics to deceive job seekers and compromise sensitive data. Let’s delve into the details of this alarming development and understand its broader implications.
The Contagious Interview Campaign: A Persistent Cyber Threat
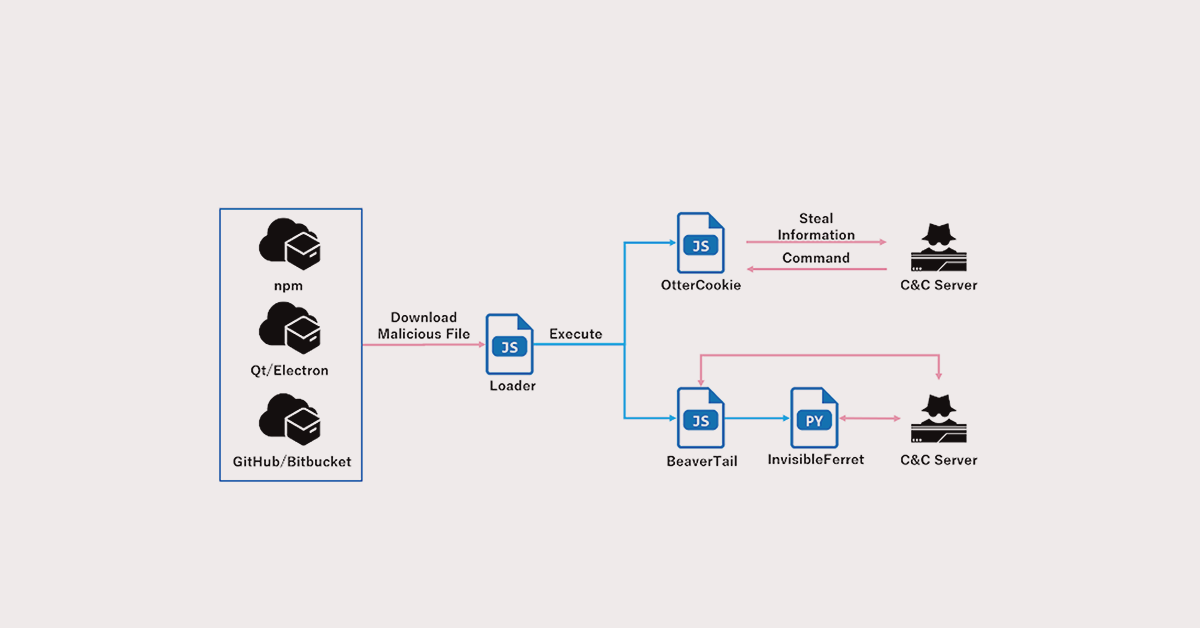
The Contagious Interview campaign, also known as DeceptiveDevelopment, relies heavily on social engineering. Hackers masquerade as recruiters, enticing job seekers with fake interview opportunities. Victims are tricked into downloading malware-laden videoconferencing apps or npm packages hosted on platforms like GitHub or official package registries. These malicious tools pave the way for the deployment of malware such as BeaverTail, InvisibleFerret, and the newly discovered OtterCookie Malware.
Palo Alto Networks’ Unit 42 first identified the campaign in November 2023, categorizing it as CL-STA-0240 and associating it with groups like Famous Chollima and Tenacious Pungsan. The campaign demonstrates how threat actors evolve their techniques to maintain effectiveness. Despite similarities with North Korea’s Operation Dream Job campaign, Contagious Interview is considered a separate, evolving threat.
To execute their attacks, these hackers leverage widely-used platforms, increasing the likelihood of success. By embedding malware into seemingly legitimate applications and repositories, they maximize their reach and minimize detection risks.
OtterCookie Malware: A Closer Look
First detected in September 2024, OtterCookie Malware exemplifies the attackers’ innovative approach. This malware communicates with a command-and-control (C2) server via the Socket.IO JavaScript library, enabling the execution of shell commands for data theft. Targeted data includes files, clipboard content, and cryptocurrency wallet keys.
Key Features of OtterCookie Malware:
- Command Execution: Runs shell commands to exfiltrate sensitive data.
- Cryptocurrency Theft: Older versions integrated cryptocurrency wallet key theft directly into the malware.
- Modular Design: Updates indicate continuous tool refinement while retaining an effective infection chain.
In addition to its data-stealing capabilities, OtterCookie Malware’s modular approach allows it to adapt quickly to specific targets. For instance, the inclusion of cryptocurrency theft demonstrates the malware’s responsiveness to emerging economic trends. This adaptability underscores the importance of proactive cybersecurity measures.
Recent Developments in the Campaign
Japanese cybersecurity firm NTT Security Holdings recently uncovered a newer OtterCookie Malware variant deployed in late 2024. While its core functionalities remain unchanged, minor implementation tweaks highlight the threat actors’ commitment to refining their methods.
The latest version features an enhanced mechanism for evading detection, ensuring it remains operational even against advanced security solutions. This persistent campaign underscores the efficacy of North Korea’s cyber operations, which blend advanced tools with deceptive tactics to target individuals and organizations globally.
Threat intelligence experts emphasize that the consistent evolution of OtterCookie Malware reflects broader trends in cybercrime, where attackers prioritize adaptability to bypass evolving defenses.
South Korea’s Crackdown on North Korean Cyber Operations
Parallel to the Contagious Interview revelations, South Korea’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs (MoFA) has imposed sanctions on 15 individuals and one organization linked to fraudulent IT schemes orchestrated by North Korea. These schemes aim to generate illicit income, steal data, and, in some cases, demand ransoms.
Key Sanctioned Entities and Individuals:
- Kim Ryu Song: Indicted by the U.S. Department of Justice for wire fraud, money laundering, and identity theft.
- Chosun Geumjeong Economic Information Technology Exchange Company: Facilitates the deployment of IT personnel abroad to fund North Korea’s nuclear and missile programs.
South Korean authorities have identified the 313th General Bureau, an entity under North Korea’s Workers’ Party, as central to these operations. This bureau oversees the overseas dispatch of IT workers who procure foreign currency through legitimate-seeming employment in Western companies.
These fraudulent IT schemes involve creating convincing identities, often using stolen information, to infiltrate reputable organizations. The revenue generated not only funds nuclear and missile programs but also perpetuates a cycle of cybercrime.
The Broader Implications of North Korea’s Cyber Activities
North Korea’s cyber campaigns are not isolated incidents. They represent a coordinated effort to exploit global systems for economic and strategic gain. The revenue generated supports the regime’s nuclear ambitions, posing a severe threat to international peace and cybersecurity.
Impact on the Cyber Ecosystem:
- Data Breaches: Theft of sensitive information from individuals and corporations.
- Economic Disruption: Illegal activities undermine legitimate economic structures.
- Global Security Risks: Funds are funneled into weapon development programs.
In addition to economic and security implications, these campaigns erode trust in digital systems. Businesses face increased costs associated with mitigating these threats, and individuals are at higher risk of identity theft and financial loss.
How to Protect Yourself from OtterCookie Malware
In light of these developments, organizations and individuals must adopt robust cybersecurity practices to mitigate risks.
- Verify Job Offers: Research potential employers and confirm the legitimacy of job-related communications.
- Secure Systems: Use up-to-date security software and implement strong password policies.
- Educate Employees: Provide training on recognizing phishing and social engineering tactics.
- Monitor Suspicious Activity: Regularly audit system logs and network traffic for anomalies.
- Engage Experts: Consider consulting with cybersecurity professionals to develop comprehensive defense strategies.
Awareness is key to prevention. By staying informed about the latest cyber threats, individuals and organizations can better protect themselves against evolving dangers.
Conclusion: A Call for Vigilance
The rise of sophisticated cyber threats like the Contagious Interview campaign highlights the need for heightened awareness and proactive defense measures. Governments, organizations, and individuals must work together to combat these threats and safeguard the global cyber ecosystem.
Collaboration among international cybersecurity agencies and private entities can help dismantle these networks. Public awareness campaigns are equally important in equipping people with the knowledge to recognize and avoid potential scams.
For further insights into cybersecurity and ways to protect your data, explore our related articles on cybersecurity best practices and social engineering attacks. Stay informed, stay vigilant, and stay secure.